Configuring Load Balancing as a Service in OpenSDN¶
- date:
2020-05-26
Overview: Load Balancing as a Service¶
Load Balancing as a Service (LBaaS) is a feature available through OpenStack Neutron. OpenSDN 1.20 and greater allows the use of the Neutron API for LBaaS to apply open source load balancing technologies to provision a load balancer in the OpenSDN system.
The LBaaS load balancer enables the creation of a pool of virtual machines serving applications, all front-ended by a virtual-ip. The LBaaS implementation has the following features:
Load balancing of traffic from clients to a pool of backend servers. The load balancer proxies all connections to its virtual IP.
Provides load balancing for HTTP, TCP, and HTTPS.
Provides health monitoring capabilities for applications, including HTTP, TCP, and ping.
Enables floating IP association to
virtual-ipfor public access to the backend pool.
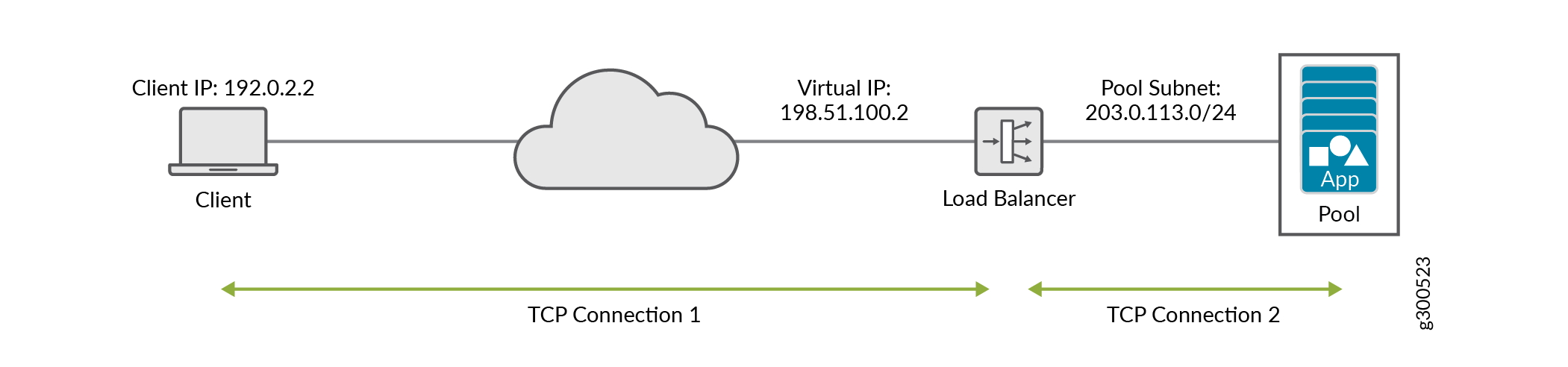
In Figure 1, the load balancer is launched with the virtual IP address 198.51.100.2.
The backend pool of virtual machine applications (App Pool) is on the subnet
203.0.113.0/24. Each of the application virtual machines gets an IP
address (virtual-ip) from the pool subnet. When a client connects to the
virtual-ip for accessing the application, the load balancer proxies
the TCP connection on its virtual-ip, then creates a new TCP
connection to one of the virtual machines in the pool.
The pool member is selected using one of following methods:
weighted round robin (WRR), based on the weight assignment
least connection, selects the member with the fewest connections
source IP selects based on the
source-ipof the packet
Additionally, the load balancer monitors the health of each pool member using the following methods:
Monitors TCP by creating a TCP connection at intervals.
Monitors HTTP by creating a TCP connection and issuing an HTTP request at intervals.
Monitors ping by checking if a member can be reached by pinging.
OpenSDN LBaaS Implementation¶
OpenSDN supports the OpenStack LBaaS Neutron APIs and creates relevant
objects for LBaaS, including virtual-ip,
loadbalancer-pool, loadbalancer-member, and
loadbalancer-healthmonitor. OpenSDN creates a service instance when
a loadbalancer-pool is associated with a virtual-ip object. The
service scheduler then launches a namespace on a randomly selected
virtual router and spawns HAProxy into that namespace. The configuration
for HAProxy is picked up from the load balancer objects. OpenSDN
supports high availability of namespaces and HAProxy by spawning active
and standby on two different vrouters.
A Note on Installation¶
To use the LBaaS feature, HAProxy, version 1.5 or greater and
iproute2, version 3.10.0 or greater must both be installed on the
OpenSDN compute nodes.
If you are using fab commands for installation, the haproxy and iproute2 packages will be installed automatically with LBaaS if you set the following:
env.enable_lbaas=True
Use the following to check the version of the iproute2 package on
your system:
root@nodeh5:/var/log# ip -V
ip utility, iproute2-ss130716
root@nodeh5:/var/log#
Limitations¶
LBaaS currently has these limitations:
A pool should not be deleted before deleting the VIP.
Multiple VIPs cannot be associated with the same pool. If pool needs to be reused, create another pool with the same members and bind it to the second VIP.
Members cannot be moved from one pool to another. If needed, first delete the members from one pool, then add to a different pool.
In case of active-standby failover, namespaces might not get cleaned up when the agent restarts.
The floating-ip association needs to select the VIP port and not the service ports.
Configuring LBaaS Using CLI¶
The LBaaS feature is enabled on OpenSDN through Neutron API calls. The following procedure shows how to create a pool network and a VIP network using CLI. The VIP network is created in the public network and members are added in the pool network.
Creating a Load Balancer¶
Use the following steps to create a load balancer in OpenSDN.
Create a VIP network.
neutron net-create vipnetneutron subnet-create –-name vipsubnet vipnet 198.51.100.2Create a pool network.
neutron net-create poolnetneutron subnet-create --name poolsubnet poolnet 203.0.113.0/24Create a pool for HTTP.
neutron lb-pool-create --lb-method ROUND_ROBIN --name mypool --protocol HTTP --subnet-id poolsubnetAdd members to the pool.
neutron lb-member-create --address 203.0.113.3 --protocol-port 80 mypoolneutron lb-member-create --address 203.0.113.4 --protocol-port 80 mypoolCreate a VIP for HTTP and associate it to the pool.
neutron lb-vip-create --name myvip --protocol-port 80 --protocol HTTP--subnet-id vipsubnet mypool
Deleting a Load Balancer¶
Use the following steps to delete a load balancer in OpenSDN.
Delete the VIP.
neutron lb-vip-delete <vip-uuid>Delete members from the pool.
neutron lb-member-delete <member-uuid>Delete the pool.
neutron lb-pool-delete <pool-uuid>
Managing Healthmonitor for Load Balancer¶
Use the following commands to create a healthmonitor, associate a healthmonitor to a pool, disassociate a healthmonitor, and delete a healthmonitor.
Create a healthmonitor.
neutron lb-healthmonitor-create --delay 20 --timeout 10 --max-retries 3 --type HTTPAssociate a healthmonitor to a pool.
neutron lb-healthmonitor-associate <healthmonitor-uuid> mypoolDisassociate a healthmonitor from a pool.
neutron lb-healthmonitor-disassociate <healthmonitor-uuid> mypool
Configuring an SSL VIP with an HTTP Backend Pool¶
Use the following steps to configure an SSL VIP with an HTTP backend pool.
Copy an SSL certificate to all compute nodes.
scp ssl_certificate.pem <compute-node-ip> <certificate-path>Update the information in
/etc/contrail/contrail-vrouter-agent.conf.# SSL certificate path haproxyhaproxy_ssl_cert_path=<certificate-path>Restart
contrail-vrouter-agent.service contrail-vrouter-agent restartCreate a VIP for port 443 (SSL).
neutron lb-vip-create --name myvip --protocol-port 443 --protocol HTTP --subnet-id vipsubnet mypool