Configuring Role and Resource-Based Access Control¶
- date:
2020-07-30
OpenSDN Role and Resource-Based Access (RBAC) Overview¶
OpenSDN supports role and resource-based access control (RBAC) with API operation-level access control.
The RBAC implementation relies on user credentials obtained from Keystone from a token present in an API request. Credentials include user, role, tenant, and domain information.
API-level access is controlled by a list of rules. The attachment points
for the rules include global-system-config, domain, and project.
Resource-level access is controlled by permissions embedded in the
object.
API-Level Access Control¶
If the RBAC feature is enabled, the API server requires a valid token to
be present in the X-Auth-Token of any incoming request. The API
server trades the token for user credentials (role, domain, project, and
so on) from Keystone.
If a token is missing or is invalid, an HTTP error 401 is returned.
The api-access-list object holds access rules of the following form:
<object, field> => list of <role:CRUD>
Where:
object—An API resource such as network or subnet.field—Any property or reference within the resource. Thefieldoption can be multilevel, for example,network.ipam.host-routescan be used to identify multiple levels. Thefieldis optional, so in its absence, the create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) operation refers to the entire resource.role—The Keystone role name.
Each rule also specifies the list of roles and their corresponding permissions as a subset of the CRUD operations.
Example: ACL RBAC Object¶
The following is an example access control list (ACL) object for a
project in which the admin and any users with the Development role
can perform CRUD operations on the network in a project. However, only
the admin role can perform CRUD operations for policy and IP address
management (IPAM) inside a network.
<virtual-network, network-policy> => admin:CRUD
<virtual-network, network-ipam> => admin:CRUD
<virtual-network, *> => admin:CRUD, Development:CRUD
Rule Sets and ACL Objects¶
The following are the features of rule sets for access control objects in OpenSDN.
The rule set for validation is the union of rules from the ACL attached to:
User project
User domain
Default domain
It is possible for the project or domain access object to be empty.
Access is only granted if a rule in the combined rule set allows access.
There is no explicit deny rule.
An ACL object can be shared within a domain. Therefore, multiple projects can point to the same ACL object. You can make an ACL object the default.
Object Level Access Control¶
The perms2 permission property of an object allows fine-grained
access control per resource.
The perms2 property has the following fields:
owner— This field is populated at the time of creation with thetenant UUID value extracted from the token.
share list— The share list gets built when the object is selected for sharing with other users. It is a list of tuples with which the object is shared.
The permission field has the following options:
R—Read objectW—Create or update objectX—Link (refer to) object
Access is allowed as follows:
If the user is the owner and permissions allow (rwx)
Or if the user tenant is in a shared list and permissions allow
Or if world access is allowed
Configuration¶
This section describes the parameters used in OpenSDN RBAC.
Parameter: aaa-mode¶
RBAC is controlled by a parameter named aaa-mode. This parameter is
used in place of the multi-tenancy parameter of previous releases.
The aaa-mode can be set to the following values:
no-auth—No authentication is performed and full access is granted to all.cloud-admin—Authentication is performed and only the admin role has access.rbac—Authentication is performed and access is granted based on role.If you are using OpenSDN Ansible Deployer to provision OpenSDN, set the value for AAA_MODE to rbac to enable RBAC by default.
contrail_configuration: . . . AAA_MODE: rbac
After enabling RBAC, you must restart the neutron server by running the service neutron-server restart command for the changes to take effect.
Note
The multi_tenancy parameter is deprecated, starting with OpenSDN
3.0. The parameter should be removed from the configuration. Instead,
use the aaa_mode parameter for RBAC to take effect.
If the multi_tenancy parameter is not removed, the aaa-mode
setting is ignored.
Parameter: cloud_admin_role¶
A user who is assigned the cloud_admin_role has full access to
everything.
This role name is configured with the cloud_admin_role parameter in
the API server. The default setting for the parameter is admin. This
role must be configured in Keystone to change the default value.
If a user has the cloud_admin_role in one tenant, and the user has a
role in other tenants, then the cloud_admin_role role must be
included in the other tenants. A user with the cloud_admin_role
doesn’t need to have a role in all tenants, however, if that user has
any role in another tenant, that tenant must include the
cloud_admin_role.
Configuration Files with Cloud Admin Credentials¶
The following configuration files contain cloud_admin_role
credentials:
/etc/contrail/contrail-keystone-auth.conf/etc/neutron/plugins/opencontrail/ContrailPlugin.ini/etc/contrail/contrail-webui-userauth.js
Changing Cloud Admin Configuration Files¶
Modify the cloud admin credential files if the cloud_admin_role role
is changed.
Change the configuration files with the new information.
Restart the following:
API server
service supervisor-config restartNeutron server
service neutron-server restartWebUI
service supervisor-webui restart
Global Read-Only Role¶
You can configure a global read-only role (global_read_only_role).
A global_read_only_role allows read-only access to all OpenSDN
resources. The global_read_only_role must be configured in Keystone.
The default global_read_only_role is not set to any value.
A global_read_only_role user can use the OpenSDN WebUI to view the
global configuration of OpenSDN default settings.
Setting the Global Read-Only Role¶
To set the global read-only role:
The
cloud_adminuser sets theglobal_read_only_rolein the OpenSDN API:/etc/contrail/contrail-api.confglobal_read_only_role = <new-admin-read-role>Restart the
contrail-apiservice:service contrail-api restart
Parameter Changes in /etc/neutron/api-paste.ini¶
OpenSDN RBAC operation is based upon a user token received in the
X-Auth-Token header in API requests. The following change must be
made in /etc/neutron/api-paste.ini to force Neutron to pass the user
token in requests to the OpenSDN API server:
keystone = user_token request_id catch_errors ....
...
...
[filter:user_token]
paste.filter_factory = neutron_plugin_contrail.plugins.opencontrail.neutron_middleware:token_factory
Upgrading from Previous Releases¶
The multi_tenancy parameter is deprecated.. The parameter should be
removed from the configuration. Instead, use the aaa_mode parameter
for RBAC to take effect.
If the multi_tenancy parameter is not removed, the aaa-mode
setting is ignored.
Configuring RBAC Using the OpenSDN WebUI¶
To use the OpenSDN WebUI with RBAC:
Set the aaa_mode to no_auth.
/etc/contrail/contrail-analytics-api.confaaa_mode = no-authRestart the
analytics-apiservice.service contrail-analytics-api restartRestart services by restarting the container.
You can use the OpenSDN WebUI to configure RBAC at both the API level and the object level. API level access control can be configured at the global, domain, and project levels. Object level access is available from most of the create or edit screens in the OpenSDN WebUI.
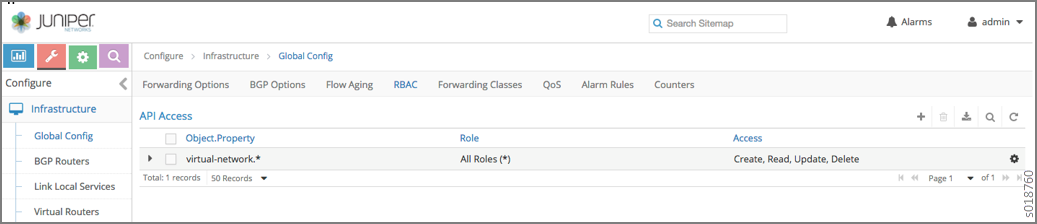
Configuring RBAC at the Global Level¶
To configure RBAC at the global level, navigate to .
Configuring RBAC at the Domain Level¶
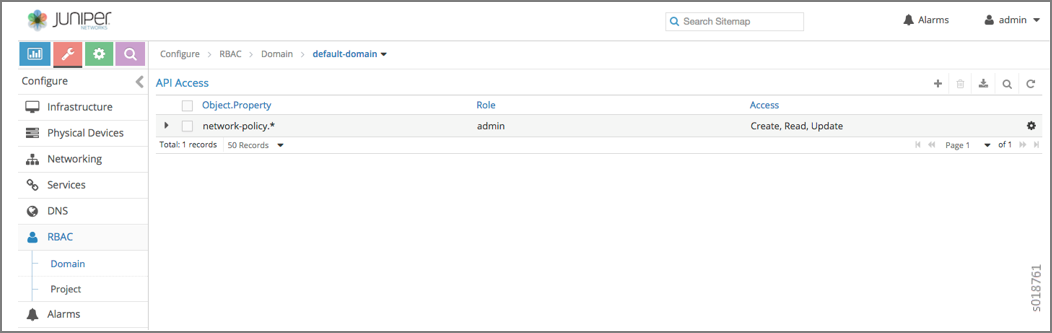
To configure RBAC at the domain level, navigate to .
Configuring RBAC at the Project Level¶
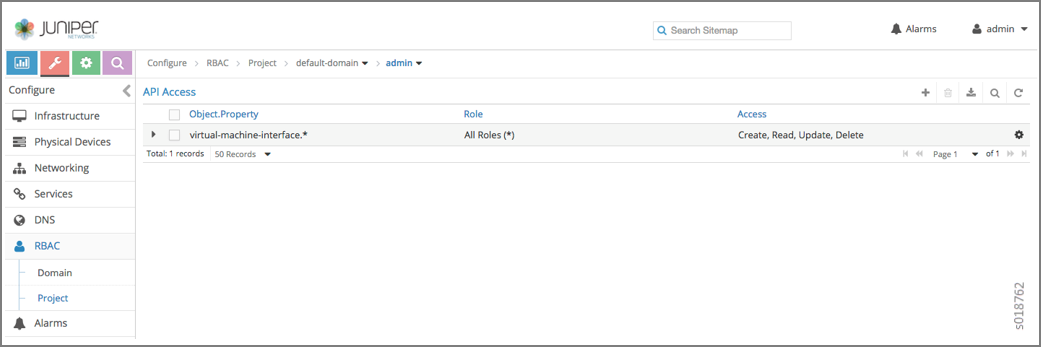
To configure RBAC at the project level, navigate to .
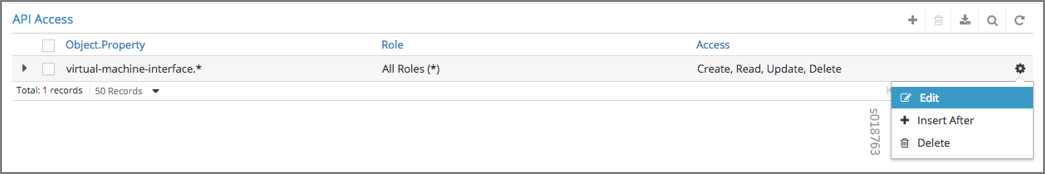
Configuring RBAC Details¶
Configuring RBAC is similar at all of the levels. To add or edit an API access list, navigate to the global, domain, or project page, then click the plus (+) icon to add a list, or click the gear icon to select from Edit, Insert After, or Delete.
Creating or Editing API Level Access¶
Clicking create, edit, or insert after activates the Edit API Access popup window, where you enter the details for the API Access Rules. Enter the user type in the Role field, and use the + icon in the Access filed to enter the types of access allowed for the role, including, Create, Read, Update, Delete, and so on.
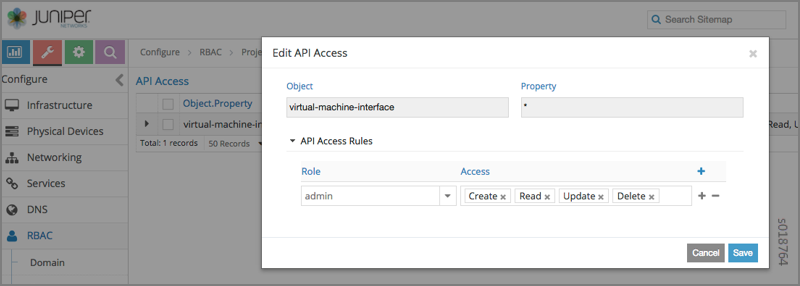
Creating or Editing Object Level Access¶
You can configure fine-grained access control by resource. A Permissions tab is available on all create or edit popups for resources. Use the Permissions popup to configure owner permissions and global share permissions. You can also share the resource to other tenants by configuring it in the Share List.
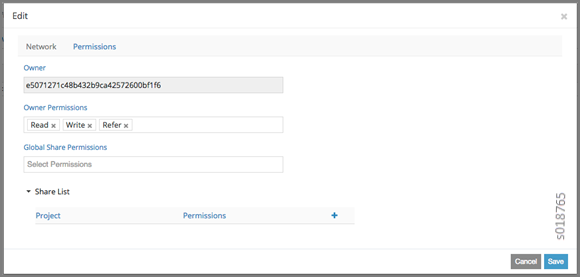
RBAC Resources¶
Refer to the OpenStack Administrator Guide for additional information about RBAC: