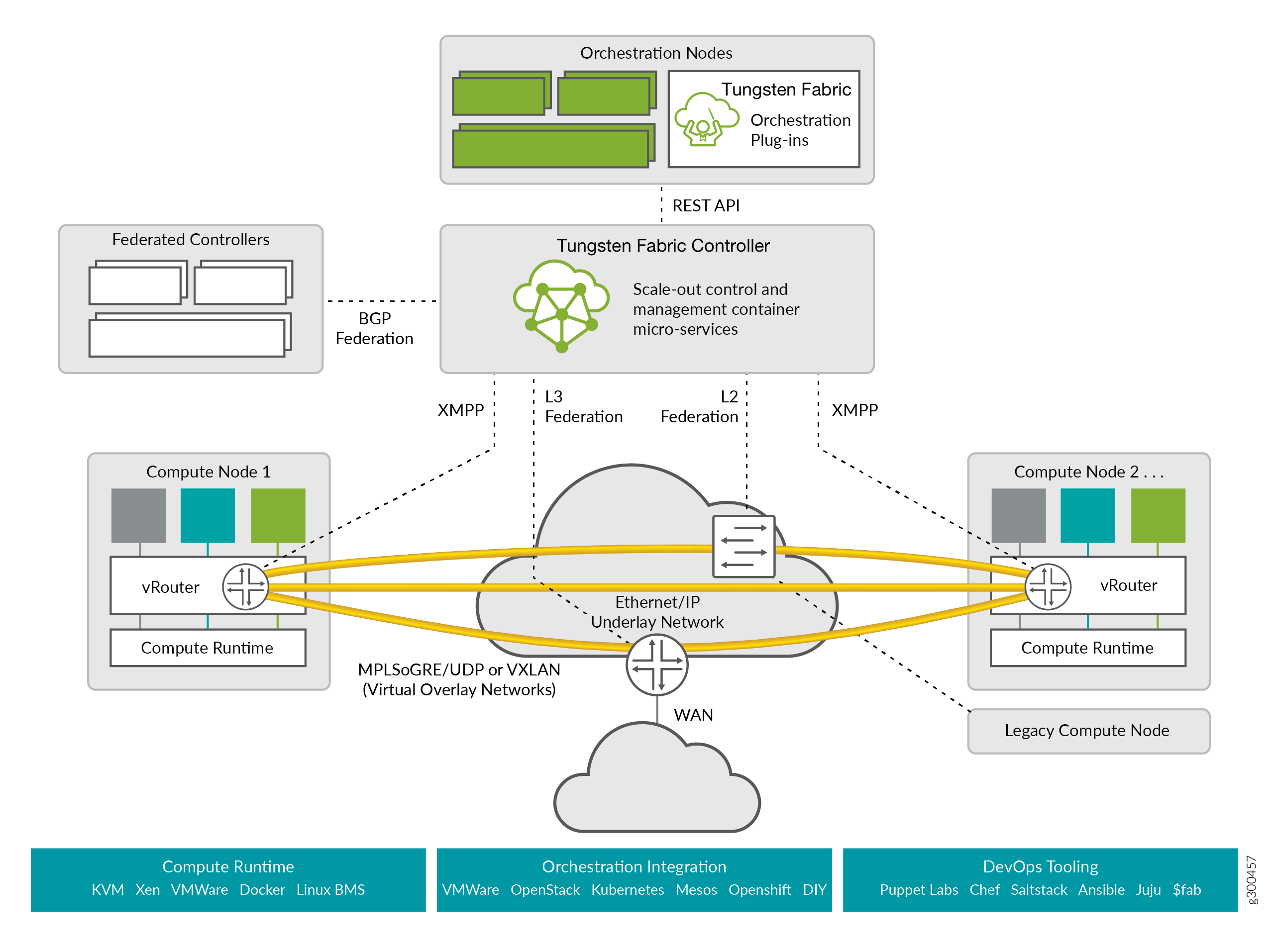
Understanding OpenSDN¶
- date:
2020-05-08
OpenSDN provides dynamic end-to-end networking policy and control for any cloud, any workload, and any deployment, from a single user interface. It translates abstract workflows into specific policies, simplifying the orchestration of virtual overlay connectivity across all environments.
It unifies policy for network automation with seamless integrations for systems such as: Kubernetes, OpenShift, Mesos, OpenStack, VMware, a variety of popular DevOps tools like Ansible, and a variety of Linux operating systems with or without virtualization like KVM and Docker containers.
OpenSDN reduces the friction of migrating to cloud by providing a virtual networking overlay layer that delivers virtual routing, bridging, and networking services (IPAM, NAT, security, load balancing, VPNs, etc.) over any existing physical or cloud IP network. It also provides multitenant structure and API compatibility with multitenant public clouds like Amazon Web Services (AWS) virtual private clouds (VPCs) for truly unifying policy semantics for hybrid cloud environments.
For service providers, OpenSDN automates network resource provisioning and orchestration to dynamically create highly scalable virtual networks and to chain a rich set of Juniper Networks or third-party virtualized network functions (VNFs) and physical network functions (PNFs) to form differentiated service chains on demand.
OpenSDN is equipped with always-on advanced analytics capabilities to provide deep insights into application and infrastructure performance for better visualization, easier diagnostics, rich reporting, custom application development, and machine automation.
OpenSDN also provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI).This GUI is built entirely using the REST APIs.